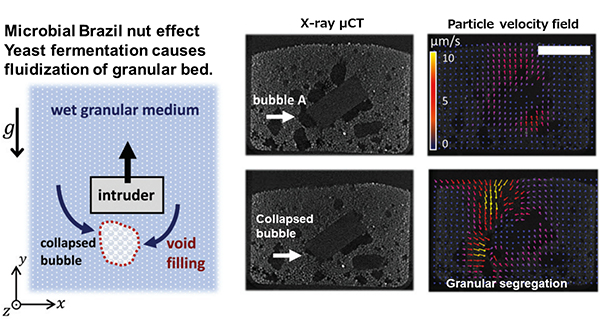
A phenomenon where microbe-generated gas bubbles create granular fluctuations at the wet sandy floors of rivers, oceans, and lakes has revealed more about the distribution of materials at the bottom of waterbodies.
Tohoku University Researchers dubbed this the "microbial Brazil nut effect." Details of their research were published in the journal Soft Matter on October 6, 2021.
The Brazil Nut Effect (BNE) happens when a granular mixture subjected to shaking results in bigger particles ending up on top. The name stems from a typical container of mixed nuts, where the larger Brazil nuts inhabit the surface and smaller nuts fall below. BNE has wide-ranging scientific applications, from boulder placement on asteroid surfaces to the pattern formation in early mammalian embryos.
The team set out to test the effects of plastic waste on the ecosystem by mixing silicon rubber into a yeast fermentation vessel. Some microorganisms use cilia and flagella to swim in water. Yeast does not. It rises to the surface at a speed of several centimeters per second by attaching itself to the bubbles it produces during the fermentation process.
Based on the team's experiments, the artificial material moved up and down from the floor of the vessel to the top, agitating the contents. As a result, nutrients were spread throughout the vessel, promoting further growth of yeast.
The researchers also discovered that microbial fermentation-induced moving transported buried materials one billion times larger than the microorganism itself.
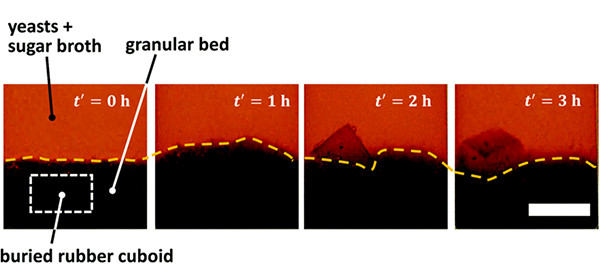
"We successfully visualized and measured the physical phenomenon of soil fluidization and the emergence of buried objects to the water surface due to particle submergence in environments where soil is deposited, such as lake bottoms, river bottoms, and seabeds," said Kenji Kikuchi, co-author of the study.
The discovery is expected to contribute to the reemergence of dormant microorganisms and viruses in the soil and further our understanding of how unknown pathogens surface.
- Publication Details:
Title: Microbial Brazil nut effect
Authors: Atul Srivastava, Kenji Kikuchi and Takuji Ishikawa
Journal: Soft Matter
DOI: 10.1039/D1SM01327K
Contact:
Kenji KikuchiDepartment of Finemechanics, Graduate School of Engineering
Email: k.kikuchi
 tohoku.ac.jp
tohoku.ac.jpWebsite: http://www.bfsl.mech.tohoku.ac.jp/


