Tin sulfide (SnS) is an abundant, safe, and environmentally friendly solar cell material. This inexpensive material is forecast to be used in next-generation solar cell panels.
A research group led by Issei Suzuki and Sakiko Kawanishi, assistant professors at Tohoku University's Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials, has fabricated n-type conductive SnS thin films by impurity doping for the first time.
Conventional SnS thin films are usually p-type conductive. Thus, SnS thin-film solar cells have been fabricated using a pn heterojunction with p-type SnS thin film and other n-type semiconductor thin films, such as CdS. However, the conversion efficiency of such heterojunction devices has stagnated at approximately 5%, rendering their use impractical.
The SnS thin-film solar cells employing a pn homojunction, which uses SnS thin films for both p-type and n-type layers, is expected to exhibit higher conversion efficiency. Yet, n-type conducive SnS thin films without toxic elements have never been achieved before.

Utilizing chlorine-doping and a sulfur plasma supply, the research group reduced the lattice defects inhibiting the n-type conversion of SnS, realizing the world's first n-type SnS thin films without toxic elements.
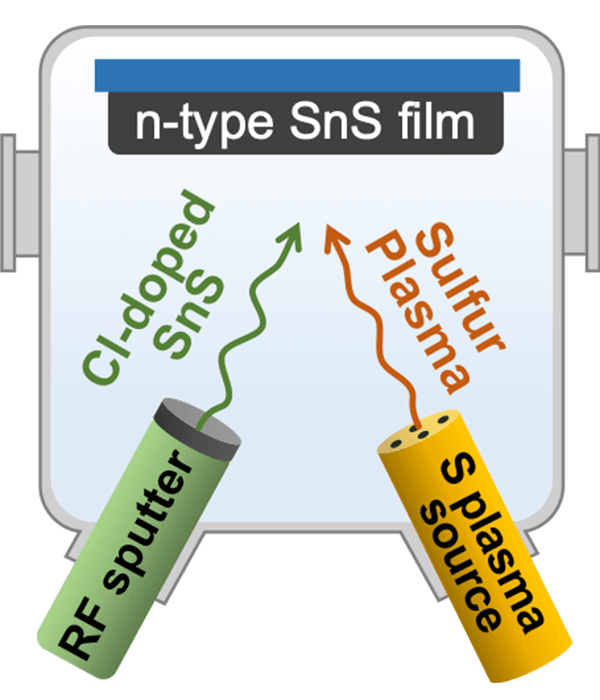
A schematic illustration of the new technique used to fabricate n-type SnS thin films. The n-type conductive SnS thin films were achieved by fabricating thin films of chlorine(Cl)-doped SnS with a supply of sulfur plasma. ©Issei Suzuki et al.
"Our realization paves the way for practical pn homojunction SnS thin-film solar cells," said Suzuki.
The results of the research were published in Physical Review Materials on December 9, 2021.
- Publication Details:
Title: N-Type Electrical Conduction in SnS Thin Films
Authors: Issei Suzuki, Sakiko Kawanishi, Sage R. Bauers, Andriy Zakutayev, Zexin Lin, Satoshi Tsukuda, Hiroyuki Shibata, Minseok Kim, Hiroshi Yanagi and Takahisa Omata
Journal: Physical Review Materials
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevMaterials.5.125405
Contact:
Issei SuzukiInstitute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials (IMRAM), Tohoku University
Email: issei.suzuki
 tohoku.ac.jp
tohoku.ac.jpWebsite: http://www2.tagen.tohoku.ac.jp/lab/omata/english/ Sakiko Kawanishi
Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials (IMRAM), Tohoku University
Email: s-kawa
 tohoku.ac.jp
tohoku.ac.jpWebsite: http://www2.tagen.tohoku.ac.jp/lab/shibata/english/


 Press release in Japanese
Press release in Japanese